Description
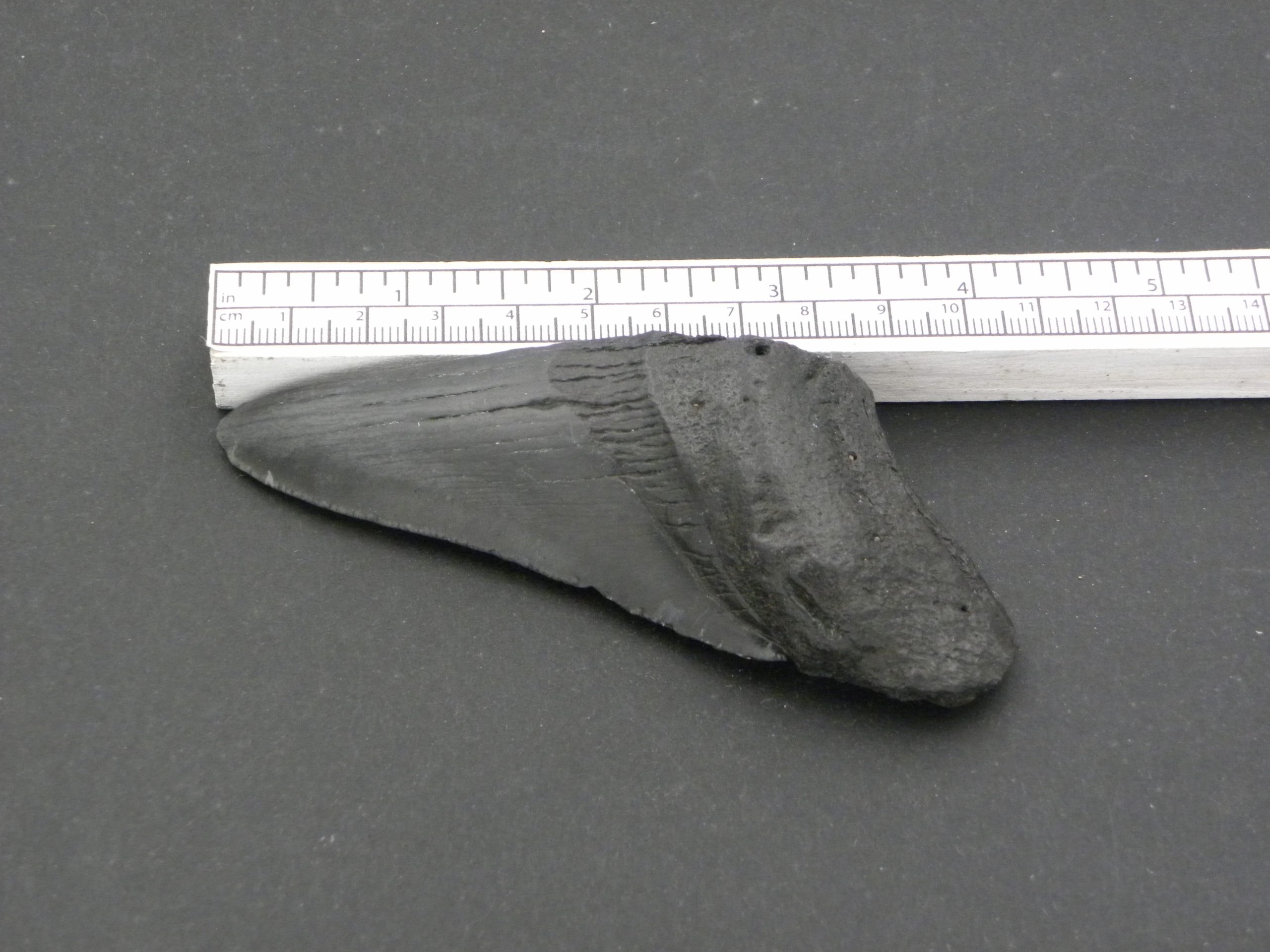
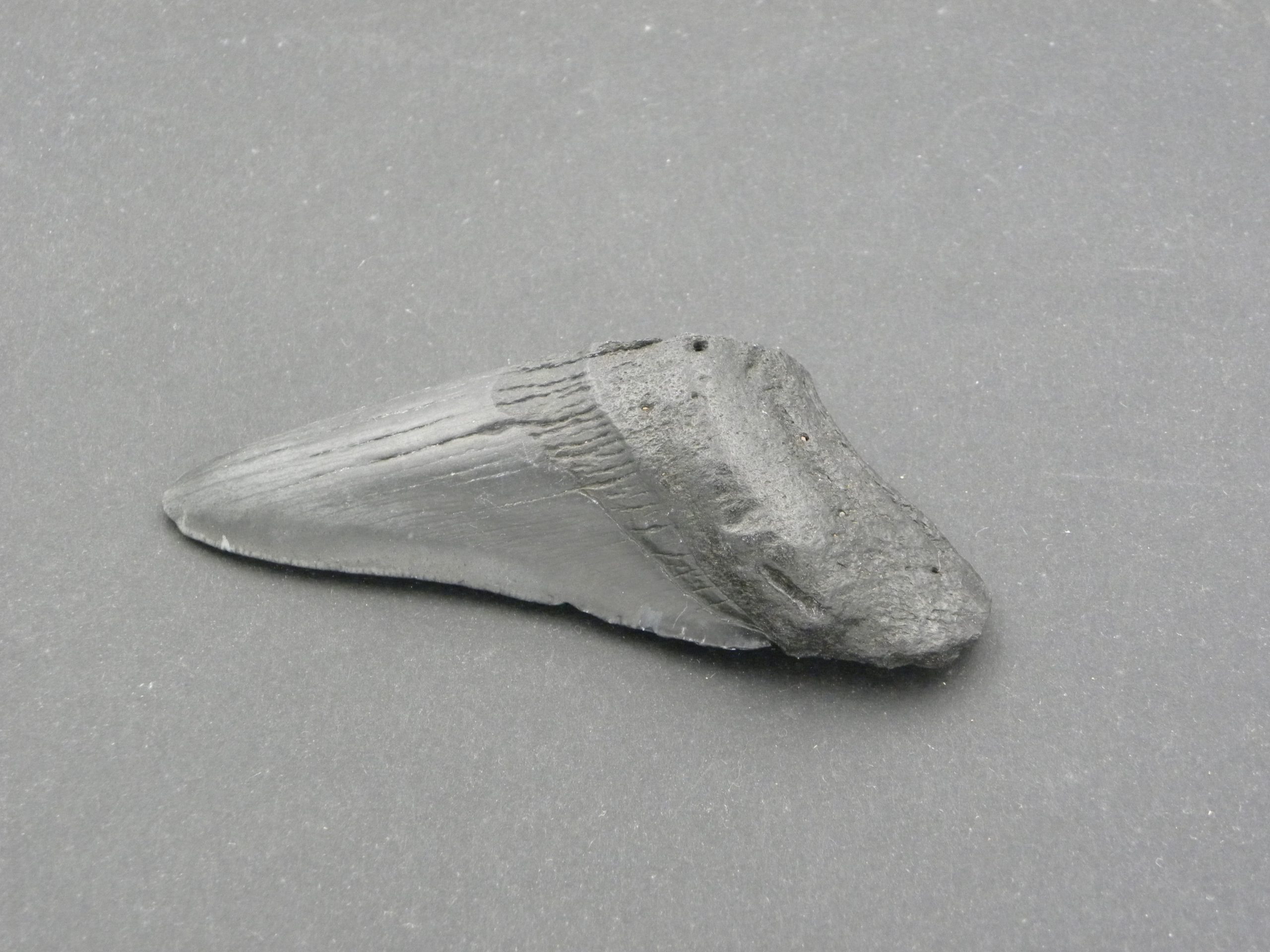
Fossilised Megalodon Sharks Tooth 8.5cm, Miocene/Pliocene
This tooth dates back to the Miocene/Pliocene period between 5-20 million years ago. The enamel is in very good condition and the the tooth is still sharp. This section of Megalodon Tooth would make an excellent addition to any fossil collection.
Megalodon sharks have been extinct for over 3 million years. The actual name Megalodon fittingly means ‘Big Tooth’. The megalodon shark preferred warmer water, with the juveniles inhabiting warm coastal areas. Current thinking suggests that cooling sea temperatures, brought on by the ice-ages, together with the lack of prey led to their eventual decline and extinction. Megalodon Sharks are considered to be one of the largest and powerful predators that have ever lived. The largest megalodon sharks grew up to 15-18 metres long with jaws up to 3 metres wide. Because sharks don’t have bones, only cartilage, it is generally only fossilised teeth that are found. The teeth of the megalogon shark are exceptionally robust. These teeth were perfect for grabbing prey and also cutting through and breaking bone.
The Great White Shark that is alive today grows to only a third of the size of the megalodon shark. There is still an ongoing debate as to whether the great white shark have evolved from the megalodon shark.
Back to Sharks Teeth, Megalodon Back To Fossils Back to Sharks Teeth, Otodus & Other